
About the Moon
The Moon is the Earth's only natural satellite. Because of the Earth's strong gravitational hold on the Moon, the same side of the Moon always faces us. This is because the Moon rotates slowly making one complete turn on its axis in just over 27 days. This is the same as its period of revolution around the Earth and thus it always presents the same hemisphere ("face") to us. The rest of the Moon is hidden from view.

Moon Data
|
Distance from Earth :
|
356 410 km to 406 685 km
|
|
Mean diameter :
|
3 473 km
|
|
Mass :
|
Approx. 1/81 of that of Earth
|
|
Surface gravity :
|
Approx. 1/6 of that of Earth
|
|
Atmosphere :
|
none - hence no clouds, weather or sound
|
|
Diurnal range of temperature at the Equator :
|
+ 200°C
|
Phases of the Moon
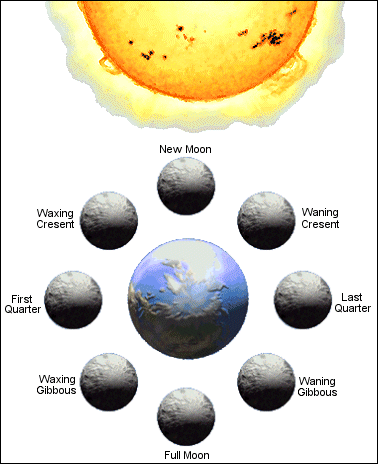
The interval between one full Moon and the next is approximately 29½ days - thus there is one new Moon and one full Moon every month. The diagram above, shows how the apparent changes in shape of the Moon from new to full arise from its changing position in relation to the Earth and both to the fixed direction of the Sun's rays.
Solar and Lunar Eclipses

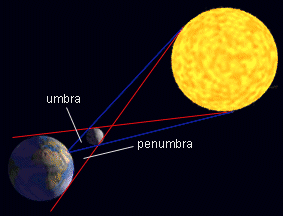
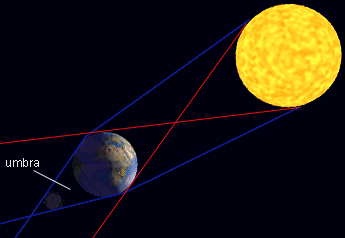
Eclipses are caused by the enormous shadows cast by the Earth and the Moon. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's shadow falls on the Earth. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth's shadow falls on the Moon. The shadow created during an eclipse has several parts. There is a region of complete shadow, known as the umbra. Surrounding the umbra is a region of partial shadow, called the penumbra. An eclipse may be total (the whole Sun or Moon is darkened) or partial (only part of the Sun or the Moon is darkened).
Solar Eclipses
An eclipse of the Sun occurs when the Moon passes directly in front of the Sun. The Moon casts a shadow that races along a narrow strip of the Earth. To an observer in the shadow's path, the Moon briefly seems to cover the Sun's disk. The period during which the Sun is totally covered can last up to 7½ minutes, but is usually shorter.
Lunar Eclipses
An eclipse of the Moon occurs when the Moon passes behind the Earth. The Moon grows dark as it enters the Earth's shadow and is no longer lighted by the Sun. Lunar eclipses occur less frequently than solar eclipses but they can be seen by more people because they can be seen wherever it is night - as long as the Moon is above the observer's horizon.


© Copyright 2002, 2003 Seelendran Naidoo
All rights reserved.
|